Observability Architecture for Cloud-Based Deployments
(IT Cloud Support Perspective)
Purpose and Context
This model represents an Observability Architecture designed to support cloud-based deployments (including containerized and microservices-based workloads) from the perspective of an IT Cloud Support Team. Its primary objective is to enable operational visibility, monitoring, alerting, and diagnostic capabilities required to ensure platform reliability, performance, and availability in AWS-hosted environments.
The architecture assumes that AWS is configured with appropriate IAM roles, policies, and trust relationships that allow the IT Cloud Support Team to perform their responsibilities securely, without granting unnecessary administrative privileges.
________________________________________
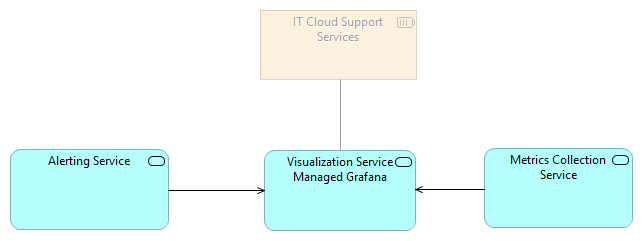
Architectural Overview
The observability architecture is centered on three core operational services:
1. Metrics Collection Service
2. Visualization Service (Managed Grafana)
3. Alerting Service
These services operate under the governance of IT Cloud Support Services, which provide operational oversight, access control, and incident response capabilities.
________________________________________
Core Components
1. Metrics Collection Service
The Metrics Collection Service is responsible for aggregating telemetry data from cloud workloads, infrastructure components, and platform services. This includes:
• Resource-level metrics (CPU, memory, disk, network)
• Application and service metrics
• Platform-level health indicators
From an AWS perspective, this service typically integrates with:
• Cloud-native telemetry sources
• Managed monitoring backends
• Service-level exporters or agents
IAM Considerations:
• Read-only access to monitoring and metrics APIs
• Permission to assume metric ingestion roles
• No modification rights to production workloads
________________________________________
2. Visualization Service (Managed Grafana)
The Visualization Service, implemented using Amazon Managed Grafana, provides a centralized dashboarding capability for the IT Cloud Support Team. It enables:
• Real-time and historical visualization of system health
• Cross-service correlation of metrics
• Operational reporting and trend analysis
Grafana acts as the primary human interface for observability data.
IAM Considerations:
• Federated access via IAM Identity Center (or equivalent)
• Role-based access to dashboards (viewer, editor, admin)
• Permissions scoped to data sources only, not underlying infrastructure
________________________________________
3. Alerting Service
The Alerting Service evaluates metrics and thresholds to detect anomalous or degraded conditions. It supports:
• Proactive incident detection
• Event-driven notifications
• Escalation to IT Cloud Support workflows
Alerts are generated based on data surfaced through the metrics and visualization layers.
IAM Considerations:
• Permission to create and manage alert rules
• Access to notification channels (e.g., email, ticketing, messaging)
• No permissions to directly remediate workloads unless explicitly delegated
________________________________________
IT Cloud Support Services (Governance Layer)
At the top of the model, IT Cloud Support Services represent the operational governance and control plane. This layer is responsible for:
• Monitoring platform health
• Responding to incidents and alerts
• Managing dashboards and alert thresholds
• Coordinating with engineering or DevOps teams
This layer does not imply full administrative control of AWS accounts.
IAM Role Design Principles:
• Least-privilege, task-oriented roles
• Separation of duties between operations and engineering
• Read-only or limited write access scoped to observability services
• Controlled role assumption with auditability
________________________________________
AWS IAM and Access Model
From an IAM perspective, the architecture assumes:
• Dedicated IAM roles for IT Cloud Support
• Explicit trust relationships allowing role assumption
• Policy boundaries that prevent infrastructure mutation
• Audit and logging of all access and actions
Typical role categories include:
• Observability Viewer
• Observability Operator
• Alert Administrator
This ensures that IT Cloud Support can observe, analyze, and respond, without introducing operational risk through excessive privileges.
________________________________________
Architectural Value
This observability architecture enables the IT Cloud Support Team to:
• Maintain situational awareness across cloud environments
• Detect and respond to incidents rapidly
• Operate independently of development teams
• Enforce governance through IAM rather than process alone
It establishes a clear operational boundary between platform support and application ownership, while ensuring that cloud-based deployments remain observable, supportable, and resilient.